Search operators are special characters and commands that extend normal keyword searches in Google. Sometimes called advanced search operators, search commands, or search parameters, they let you refine or filter results in ways plain keywords can't.
Most users only type words into the search box. But operators like site:, " " (exact match), - (exclude), and OR can dramatically narrow or expand what Google shows. They're useful for research, technical SEO audits (check out our 2026 technical SEO checklist), content discovery, competitive analysis, and finding files like PDFs.
Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) are a broader concept used in databases and search engines. Google supports many of them in a simplified way, which we'll cover in detail below.
TL;DR
Search operators are commands you add to Google queries to control what appears in results. They let you filter by site, file type, date, and where keywords appear, turning vague searches into precise ones. Google supports simplified Boolean logic compared to academic databases. You can use operators for everyday searches, SEO audits, competitor research, and discovering long-tail keywords. The goal isn't memorizing dozens of operators, it's understanding the core ones that solve real problems and learning to combine them strategically.
What Are Search Operators in Google?
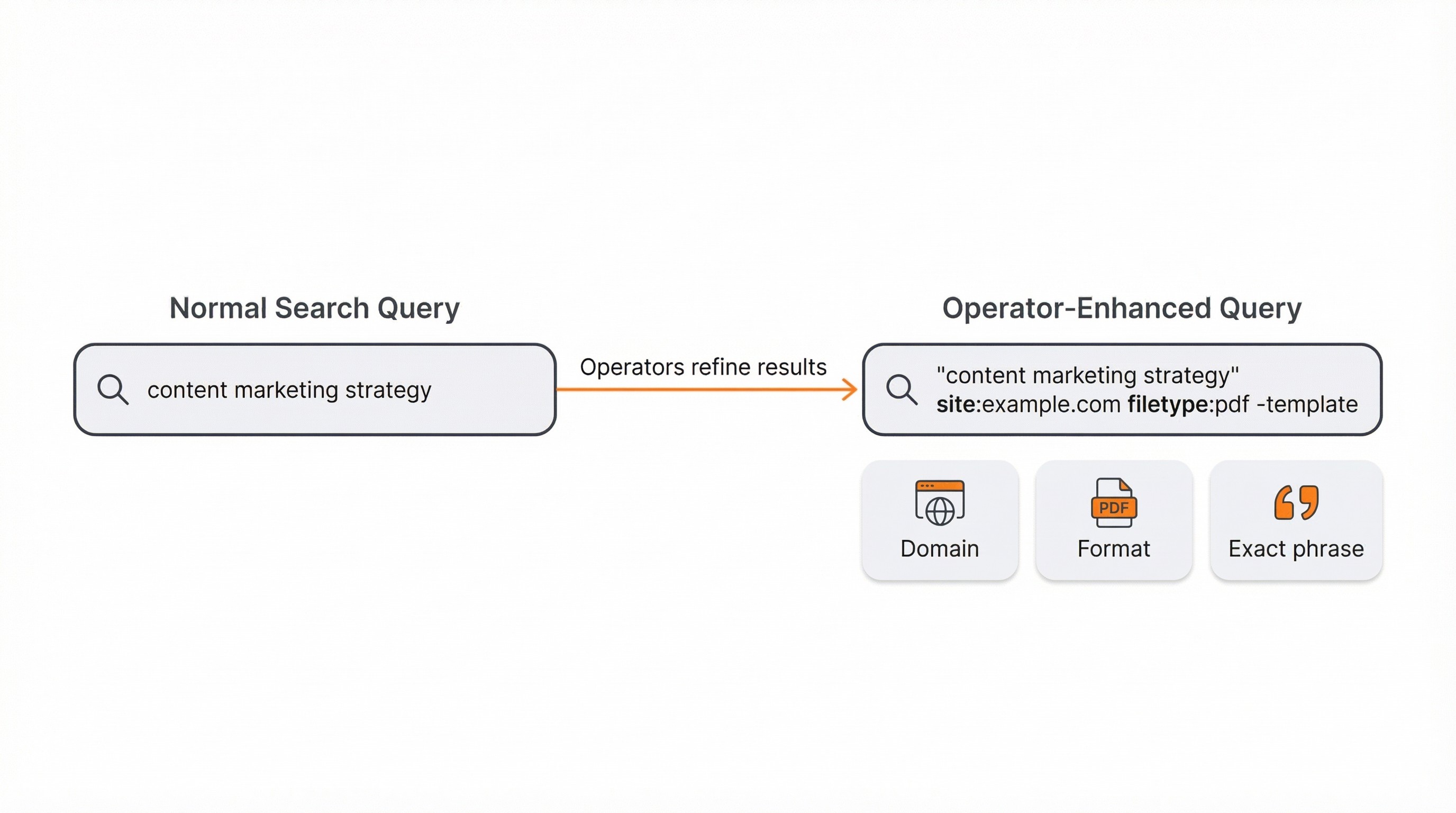
Google search operators are special characters and commands you add to a query to extend what simple keyword searches can do. They filter by site, file type, title, or date, letting you control exactly where keywords appear and which results to exclude.
The most practical ones:
Quotes
"keyword phrase"force exact phrase matchesMinus
-keywordexcludes any result containing that termSite
site:example.comlimits results to one domain or subdomainFiletype
filetype:pdffinds specific document formats
Operators get labeled "basic" (quotes, minus, OR, wildcard *, parentheses) versus "advanced" (site:, intitle:, inurl:, before:, after:). The distinction matters less than understanding which ones actually work and which have been deprecated.
Some operators like link: and info: have been deprecated and should not be relied on for SEO or research. Stick with what major SEO tools like Moz confirm works in 2025.
Boolean vs Search Operators
Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) are logical connectors used in databases and library catalogs. Google supports them but simplifies the syntax:
Operator | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
AND | Results must contain all terms | marketing AND automation |
OR | Results may contain either term | college OR university |
NOT / AND NOT | Exclude a term | football NOT soccer |
Google treats spaces as implicit AND, so "marketing automation" already requires both terms. You only need to capitalize OR when you want alternatives: Ahrefs OR Moz returns pages mentioning either tool.
For exclusion, Google uses minus - instead of NOT. So apple -iphone excludes iPhone results.
Google search operators go beyond Boolean logic. Commands like site:, intitle:, inurl:, before:, and after: don't exist in traditional Boolean syntax. They're Google-specific filters for targeting where keywords appear or limiting by domain and date.
Academic databases require explicit Boolean syntax with parentheses: (climate change) AND (policy OR regulation). Google is simpler but less precise.
Need help implementing these strategies for your business? Our SEO services include technical audits, keyword research, and competitive analysis using advanced search operators and professional tools.
Google Search Operators Cheat Sheet (50 Commands)
This comprehensive table covers 50 operators, including working commands, unreliable ones, and retired operators you might see in older guides.
Operator | Type | What it does | Example query |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | Finds results containing the exact phrase in quotes. |
|
| Basic | Finds results containing both terms (implicit AND). |
|
| Basic | Explicitly requires both terms to appear. |
|
| Basic | Finds results containing either term or both. |
|
| Basic | Groups logic to combine OR with other terms. |
|
| Basic | Excludes results containing the keyword. |
|
| Basic | Excludes results containing that exact phrase. |
|
| Basic | Acts as a placeholder for one or more words. |
|
| Basic | Matches phrases where wildcard fills the gap. |
|
| Basic | Searches for numbers in a specified range. |
|
| Basic | Helps surface prices in some commerce‑oriented queries. |
|
| Basic | Similar to |
|
| Restrict | Limits results to a specific domain or subdomain. |
|
| Restrict | Limits results to a specific subdomain only. |
|
| Restrict | Limits results to a specific directory. |
|
| Discovery | Finds sites Google considers similar to a domain. |
|
| On‑page | Requires keyword to appear in the page title. |
|
| On‑page | Requires all listed words in the title, in any order. |
|
| URL | Requires keyword to appear in the URL. |
|
| URL | Requires all listed words to appear in the URL. |
|
| Content | Prioritizes results with keyword in the body text. |
|
| Content | Requires all words to appear in the body text. |
|
| File | Restricts results to a specific file type. |
|
| File | Alias for |
|
| Utility | Shows dictionary‑style definition cards. |
|
| Utility | Displays Google’s cached copy of a page (where available). |
|
| News | Filters Google News results by news source. |
|
| Date | Shows results indexed as older than the given date. |
|
| Date | Shows results newer than the given date. |
|
| Date | Restricts results to a date range. |
|
| Proximity | Finds terms within X words of each other (undocumented but still works; test queries). |
|
| Instant answer | Shows current weather for a location. |
|
| Instant answer | Shows local time for a location. |
|
| Instant answer | Shows stock information for a ticker symbol. |
|
| Maps | Opens map results for a location. |
|
| Media | Shows info about a movie. |
|
| Utility | Converts units directly in search. |
|
| Utility | Converts one currency to another. |
|
| Social | Searches for results related to a social handle. |
|
| Social | Searches for content containing a hashtag. |
|
| Domain pattern | Searches all subdomains or wildcard matches for a TLD. |
|
| News | Filters some news queries by location context. |
|
| Anchor (limited) | Filters pages that have the keyword in inbound anchor text (heavily sampled). |
|
| Anchor (limited) | Requires all words in inbound anchor text (limited/reduced but still works in some tests). |
|
| Combo | Site search combined with exact phrase matching. |
|
| Combo | Site search with phrase in the title. |
|
| Combo | Site search restricted to specific filetype. |
|
| Combo | Exact‑match OR logic for alternative phrases. |
|
| Combo | Exact phrase, term exclusion, and site restriction together. |
|
Each operator filters results differently. Quotes lock in exact phrasing. Minus removes noise. site: narrows results to one domain. filetype: targets document formats. Stick with the reliable ones and skip anything marked as deprecated or unreliable.
Practical Examples
Government documents: site:irs.gov child tax credit filetype:pdf finds official IRS PDFs about the child tax credit, cutting through blog posts and news articles to get straight to the source.
Recent policy updates: after:2024-01-01 "electric vehicle tax credit" site:energy.gov surfaces recent Department of Energy updates about EV incentives, useful when policy changes frequently.
Guest posting opportunities: intitle:"write for us" inurl:write-for-us marketing -site:medium.com discovers marketing sites seeking contributors, excluding Medium from results.
Stack operators strategically to find what you need in one search instead of ten.
Advanced Search Operators for SEO
If you're working in SEO, search operators become diagnostic tools. They help you audit sites, find content gaps, spot technical issues, and uncover link building opportunities without relying entirely on paid software.
Indexing and Technical Audits
Check what's indexed: Run site:yourdomain.com to see everything Google has indexed. You might discover staging URLs, old subdomains, or pages that shouldn't be public.
Find specific file types: Use site:yourdomain.com filetype:pdf to see which PDFs Google has indexed. You might find old documents or duplicate content you didn't know existed.
Audit HTTP pages: Search site:example.com -inurl:https to find non-secure URLs still indexed on your domain. These can hurt trust signals and rankings.
Content Protection
Spot plagiarism: Take a unique sentence from your article, wrap it in quotes, and search allintext:"unique sentence from your article". If someone copied your content verbatim, this surfaces it quickly.
Link Building Opportunities
Find resource pages: Search [topic] intitle:resources inurl:resources to locate curated lists of tools, articles, or services in your industry. These pages often accept new submissions if your content fits.
Discover guest post sites: Try intitle:"write for us" inurl:write-for-us [topic] to find sites actively seeking contributors.
Locate review roundups: Use allintitle:review (brand1 OR brand2) to find comparison articles that might feature your product.
Competitive Research
Identify similar sites: The related:competitor.com operator shows sites Google considers similar to your competitor. This helps you map your competitive landscape and find sites to analyze or target for partnerships.
Validation and Limitations
Many SEOs combine operators with tools like Ahrefs or Moz. Use operators to surface a list of potential link targets, then check those domains in Ahrefs to see their Domain Rating, organic traffic, and backlink profile before deciding which ones are worth outreach.
Some operators that used to work reliably, like inanchor:, allinanchor:, and AROUND(X), now produce inconsistent results. Use the ones major SEO resources confirm still work, and validate important findings with dedicated tools instead of relying entirely on operator results.
Site Search Operators: Searching Within One Website
The site: operator limits results to a single domain or subdomain, turning Google into a better way to search most websites than their own search boxes.
Everyday Uses
News articles: site:nytimes.com "student loan forgiveness" pulls up every New York Times article on the topic, organized by Google's relevance algorithm instead of the Times' internal search.
Forum discussions: site:reddit.com "freelance writer rates" surfaces Reddit discussions about pricing without wading through marketing content or sponsored posts.
SEO Applications
Internal linking audits: site:yourdomain.com "email marketing" finds every page mentioning email marketing. Useful for locating older posts that should link to your new comprehensive guide.
Competitor research: site:competitor.com "pricing" shows how competitors structure their pricing pages. You might discover tiered plans, product bundles, or positioning angles worth analyzing.
Government documents: site:govinfo.gov "climate policy" filetype:pdf accesses US government PDFs directly, bypassing clunky website search interfaces.
Combining Site Search with Other Operators
The real power comes from stacking operators. site:cdc.gov intitle:"flu" after:2024-01-01 surfaces recent CDC pages with "flu" in the title, published after January 2024. This precision is hard to achieve with most website search tools.
Large sites and government databases often have terrible internal search. Site operators solve that problem. They're also useful for competitor research, content gap analysis, and finding specific content types on poorly organized sites.
Combining Operators and Keywords Effectively
Single operators are useful. Combining them is where you find exactly what you need in one search instead of ten. Stack operators that each solve a different part of your search problem. Need content about email marketing, published on a specific blog, with a particular keyword in the title? That's three filters working together.
Effective Combinations
Topic + site + title: site:blog.example.com intitle:"email marketing" "welcome sequence" finds articles on a specific blog about email marketing that also mention welcome sequences. You're narrowing by domain, title content, and body content simultaneously.
Topic + OR logic: (copywriting OR "content writing") "freelance rates" searches for pages discussing freelance rates in either copywriting or content writing contexts. The parentheses group the OR logic so Google reads it correctly.
Competitor + exclusion: "best project management tools" -asana -trello surfaces listicles and comparison articles that don't mention Asana or Trello. If you're launching a competing tool, these lists might be more open to adding a new option.
Local research: "coffee shop" "Austin TX" map: forces Google to show map results for coffee shops in Austin, useful when you want location-based information rather than articles about coffee shops.
Parentheses help when you're using OR logic or combining multiple conditions. (laptop OR desktop) deals under $500 makes it clear you want deals for either device type, not pages that mention all those terms separately.
Keep queries realistic. You can technically chain 10 operators into one massive query, but that often produces zero results or forces Google to ignore some of your filters. Start with 2 to 3 operators that directly address your search goal, then add more only if you're still getting too much noise.
Using Search Operators to Find Long-Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific search phrases with lower search volume and competition but higher conversion potential. Instead of ranking for "SEO," you rank for "how to optimize blog posts for local SEO."
Research shows about 91.8% of keywords are long-tail. They're easier to rank for, have clearer search intent, and align better with what people actually type when they're ready to take action.
Search operators help you discover these phrases by showing you how real people talk about topics on forums, Q&A sites, and competitor blogs.
What Works
Explore question patterns: "how to" * "search operators" fills in the wildcard with common phrases like "how to use Google search operators" or "how to master search operators." Each variation is a potential long-tail keyword.
Site scrape competitors: site:competitor.com "search operators" pulls up every page where they mention the topic. Read through their titles and content to see which angles they target.
Mine question-style queries: site:quora.com "Google search operators" or site:reddit.com inurl:"/question/" "SEO keyword research" surfaces actual questions people ask. These reflect genuine search intent.
Combine with dates or filetypes: after:2024-01-01 "keyword research" site:.edu filetype:pdf finds recent academic content that reveals terminology not in commercial keyword tools.
Most SEOs pair this with tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush. Operators give you real-world phrasing. Tools give you search volume and keyword difficulty.
Example: try site:reddit.com "local SEO for" * to find questions like "local SEO for dentists," "local SEO for lawyers," "local SEO for restaurants." Each is a niche you can research further.
Practical Examples: Everyday, Research, and SEO Use Cases
Everyday Searches
Price range filtering: laptop $500..$800 "best value" attempts to filter results by budget. Google's price range operator isn't always reliable, but it's worth trying when you're comparison shopping.
Local business reviews: site:yelp.com "coffee shop" "Brooklyn, NY" pulls Yelp reviews for coffee shops in a specific neighborhood, cutting through all the generic "best coffee in Brooklyn" listicles.
Academic and Research
Scholarly sources: "climate change" AND "policy" site:.gov filetype:pdf finds US government reports that discuss both climate change and policy. The .gov domain filter ensures you're getting official sources, and the PDF filetype often indicates formal reports rather than web pages.
Quick definitions: define:heuristics gives you a dictionary-style definition right in the search results, useful when you're reading research papers and encounter unfamiliar terms.
SEO and Marketing
Competitor content gaps: site:competitor.com intitle:"what is" "search operators" identifies definition-style content your competitor has published. If they've covered "what is X" topics you haven't, that's a potential gap in your own content strategy.
Internal linking audits: site:yourdomain.com "email marketing tips" finds every page on your site mentioning email marketing tips. If you've just published a comprehensive email marketing guide, you can use this list to identify pages that should link to it, strengthening your internal link structure and helping the new guide rank.
Common Mistakes and Limitations
Search operators have limitations. Know what they can't do so you don't draw wrong conclusions from incomplete data.
Retired Operators
Google has officially dropped several operators that used to work. link:, info:, and phonebook: search no longer function as originally documented. If you see older guides recommending these, those instructions are outdated.
Unreliable Operators
Other operators are technically still available but produce inconsistent results. AROUND(X), inanchor:, allinanchor:, and daterange: might work sometimes, but you can’t count on them for important research or audits.
Results Are Approximate
Operator results aren't comprehensive. Google personalizes search results based on location, search history, and dozens of other factors. The results you see for site:yourdomain.com might not include every single indexed page. Date filters rely on when Google indexed or updated a page, not necessarily when it was published.
Validate with Dedicated Tools
Use operators as practical shortcuts, not as precise analytics tools. If you're doing serious SEO work, validate important findings with dedicated software. Screaming Frog for crawl analysis, Google Search Console for actual index status, Ahrefs or SEMrush for backlink data. Operators help you spot patterns and surface issues quickly, but they don't replace comprehensive tools when accuracy matters.
Apply What You've Learned
Test three operator combinations this week on a topic you're researching or a site you manage. Pick one basic combination like site:yourdomain.com intitle:"keyword", one competitor research query, and one long-tail keyword discovery pattern with wildcards. See how much faster you find relevant results compared to plain keyword searches.
If your team does regular SEO or content work, build a small internal playbook of go-to operator queries. Document the combinations that consistently surface useful information for indexing checks, content gaps, or link opportunities. This turns operators into a repeatable research process instead of random tricks.
Once you're comfortable with operators, explore how dedicated keyword research and SEO tools extend these capabilities. Tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Moz combine operator-style filtering with data you can't get from Google: search volume, keyword difficulty, backlink profiles, and traffic estimates. Operators teach you how to ask better questions. Tools give you the data to answer them at scale.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are search operators in Google search?
Search operators are special commands you add to queries to control what appears in results. Use quotes " " for exact matches, minus - to exclude terms, site: to search one domain, and filetype: to find specific document types. They refine results by constraining how Google interprets your query and where it looks for your terms (for example, in titles, URLs, or body text), giving you more control than a plain search.
How do I use Google search operators for SEO?
Run site:yourdomain.com to check what Google has indexed. Use site:competitor.com intitle:"topic" to analyze their content. Use exact‑match quotes from your articles to spot potential copies, but confirm manually because legitimate quotes and partial matches can also appear. Discover guest post opportunities with intitle:"write for us" plus your topic.
Which advanced search operators help narrow search results?
Use quotes " " for exact phrases, minus - to exclude noise, site: for one domain, intitle: for title keywords, and before:/after: for date ranges.
What is the best way to search for an exact phrase on Google?
Put quotes around it: "exact phrase here". Google matches those words in that order. Combine with other operators for precision: site:example.com "exact phrase" searches one domain, intitle:"exact phrase" requires it in page titles. This works for finding specific content, checking competitor coverage, or spotting plagiarized material.
How can I use site search operators to search within one website?
Type site:example.com followed by keywords. Add filetype:pdf for documents, intitle: for title matches, or after:2024-01-01 for recent content. Example: site:competitor.com intitle:"pricing" shows their pricing pages.



